Walrus Evolution, part 1
Walrus Evolution, part 2
Walrus Evolution, part 3
Walrus Evolution, part 5
“The Walrus (Trichechus rosmarus) is a very fat, clumsy brute, much uglier than his picture, with a coarse, oily skin all wrinkled and scarred; long, protruding tusks; bristly whiskers and scuffling flippers that barely serve to move his bulky body over the land. In the water he is more at home, and though it does not require a high degree of strength and skill to dig clams, that being his daily occupation, yet he is able to keep very fat on the fruits of his industry and has much leisure to swim about or doze on ice floes and sea beaches.” – Dane Coolidge, Birds and Nature 10:2, September 1901
First introductory note: I have varied so far in writing in
a chronological order in terms of the history of research or phylogenetic order
(e.g. up the cladogram one node at a time). However, because the majority of
non-odobenine odobenids (e.g. “Imagotariinae” and Dusignathinae) were not
recognized as walruses until the 1970’s, only the odobenines were recognized as
walruses during the early history of fossil walrus research. Because of this,
the story of odobenines can largely be told in chronological order.
Second introductory note: This is by far and away my longest
post ever on coastal paleo, so bear with me – save a half hour, or bookmark the
page and come back. More has been published on odobenines than the rest of the
odobenids combined, so there is quite a lot to summarize – and I think it’s
quite a fascinating story.
The unfortunate taxonomic history of Alachtherium
The first fossil walrus was described
in the mid 19th century by Du Bus (1867) and named Alachtherium
cretsii based upon a well-preserved mandible from the lower Pliocene
Scaldisian sands of Belgium.
This mandible shares several features with modern Odobenus including an
elongate mandibular symphysis and small coronoid process, a lower canine that
is reduced to the same size as the cheek teeth, and incisors that are
positioned anterior to the canine and in line with the toothrow (rather than
medial to the canine). However, the mandible differs in its much larger size, having
an upturned and unfused symphysis, and primitively retaining a fourth lower
premolar (lost in Odobenus, which only has p1-3). Van Beneden (1877) later
referred a partial braincase and humerus to the species, but Rutten (1907)
thought the braincase and mandible were incompatible and erected a new taxon
for the braincase, Trichechus antverpiensis*. This braincase is also
larger than modern Odobenus rosmarus, and differs principally in having
a rectangular dorsal margin in posterior view. Further unnecessary
complications arose when Hasse (1910) described some partial skulls and
postcrania of several individuals from the slightly younger, upper Pliocene
Merxemian sands, which he named Alachtherium antwerpiensis (note: antverpiensis
versus antwerpiensis) as he also considered the new material
incompatible with the type.
*Note that early workers
often included walrus in the genus Trichechus, which is the genus that
the manatees belong in; most recent works do not discuss the errors of earlier
workers, and a bit of searching on google has failed to enlighten me any
further. I assume that superficial similarities such as blubber and a short
muzzle as well as bottom feeding contributed to the confusion of earlier
workers. However, Linneaus originally got it right by naming the species Phoca
rosmarus – obviously not a phocid in the modern sense, but Linneaus placed
practically all pinnipeds within the genus Phoca, so at least he
recognized the pinniped affinities of the walrus.
Beautiful illustrations of the holotype mandible and referred braincase (in posterior view) of Alachtherium cretsii, (Pliocene Scaldisian Sands, Belgium) from Van Beneden (1877). Thanks to Olivier Lambert for the excellent scan of this work.
Before we return to the complicated taxonomic history of Alachtherium,
another discovery was made around the turn of the century in Virginia:
a new walrus, also based on a lower jaw, was named by Berry
and Gregory (1906) as Prorosmarus alleni. The fossil jaw was collected
from the lower Pliocene Yorktown Formation, and is similar to both Odobenus and
Alachtherium cretsii in having a less-upturned ramus as in the former,
but again having an unfused symphysis as in the latter as well as primitively
retaining a lower fourth premolar, which (along with the lower molar) is
missing in Odobenus.
The holotype mandible of Prorosmarus alleni, (Pliocene Yorktown Formation, Virginia) photographed at the Smithsonian.
For the rest of the 20th
century, work on Pliocene walruses assignable to Alachtherium was
monopolized by European researchers. Van der Feen (1968) described some new cranial
material which he assigned, without explanation, to T. antverpiensis,
which he placed in Odobenus (as Odobenus antverpiensis); this was
done without explaining why the fossil was not assignable to either species of Alachtherium.
Later work by Erdbrink and Van Bree (1990) figured and described a beautiful,
complete, and gigantic skull dredged from the seafloor off the Dutch coast
which they similarly identified as Odobenus antverpiensis. Erdbrink and
Van Bree (1986, 1990) considered virtually all Pliocene walruses to belong in
the genus Odobenus and assigned all specimens from the North
Atlantic to O. antverpiensis, identifying other species Trichecodon
huxleyi (see below), Trichecodon koninkii (see below), and Alachtherium
cretsii as nomina nuda* as well as (rightfully) questioning the
generic distinctiveness of Prorosmarus.
The skull of Alachtherium
cretsii (see below) reported by Erdbrink and Van Bree (1990, as O.
antverpiensis) is large (a bit larger than extant Odobenus), and
bears large canine alveoli indicating the presence of tusks that are slightly
anteriorly sloping, unlike the vertical tusks of extant Odobenus. The
skull also has a somewhat elongate rostrum (as opposed to the blunt and
inflated rostrum of Odobenus), and possesses more teeth than Odobenus:
the modern walrus lacks incisors and an upper molar, and these teeth are
primitively retained in Alachtherium. A single postcranial feature
unites Alachtherium with the modern walrus: a deltoid insertion on the
humerus that is separated from the deltopectoral crest (in other pinnipeds and
non-odobenines, the deltoid insertion is positioned on the crest and not easily
identifiable). As it turns out, humeral morphology is fairly diagnostic in
walruses (more on this below).
*Nomen nudum means a “naked
name”: a name that has been proposed but an insufficient description or
diagnosis has been used. In all three cases these names satisfy the minimum
requirements for being valid names under ICZN rules and thus this was a bit of
a taxonomic faux-pas on behalf of Erdbrink and Van Bree. However, they were
right to question the distinctiveness of T. huxleyi and T. koninckii
(see below), but Alachtherium cretsii is clearly a good name with a
well-preserved, readily diagnosable (and, historically diagnosed and
well-figured) type specimen. However, the plot thickens – so read on…
Well-preserved skull of Alachtherium cretsii dredged from the North Sea offshore of the Netherlands (Pliocene), from Post (2004).
In 1994, San Diego Natural History
Museum curator Tom Deméré published two papers, one of which described the
dusignathine Dusignathus seftoni (see previous post) and also the bizarre
odobenine Valenictus chulavistensis (see below). The second paper was a
phylogenetic analysis and revision of the Odobenidae, and he summarized much of
the prior work on North Atlantic Pliocene walruses. He indicated that the large
skull assigned to “Odobenus antverpiensis” by Erdbrink and Van Bree
(1990) uniquely shares a rectangular outline of the braincase in posterior view
with braincases figured by Van Beneden (1877), Rutten (1907), and Hasse (1910),
previously assigned to either T./O. antverpiensis (Rutten, 1907) or Alachtherium
antwerpiensis (Hasse, 1910). Deméré (1994) concluded that insufficient
evidence existed to distinguish between two (or three, for that matter) species
of Alachtherium, and synonymized all with Alachtherium cretsii,
noting that Prorosmarus alleni may also fall victim to synonymy.
In defense of this lumping, Deméré (1994) noted that all the material is
relatively larger than extant Odobenus and the toothrow of the skull and
mandible are both sinuous and matching in profile. He further indicated that two
species of Alachtherium may be a defensible hypothesis considering that
the material reported by Hasse (1910: named as A. antwerpiensis) is late
Pliocene in age as opposed to the early Pliocene age of the holotype A.
cretsii mandible. Deméré (1994) further noted that the skull reported by
Erdbrink and Van Bree (1990) has four postcanine teeth as opposed to five in
the A. antwerpiensis skull described by Hasse (1910), and that the
former specimen retains a medial incisor whereas it is lost in the latter.
A curious recent
development was a popular article by Klaas Post (2004) who agreed with studies
by Deméré (1994) and Kohno et al. (1995) in assigning Pliocene North Atlantic
walruses to Alachtherium cretsii. Despite this rather sober taxonomic
opinion, Post (2004: page 70) explained that “even Americans (Deméré, 1994)
and the Japanese (Kohno et al., 1995)” have contributed to the “babylonian
confusion” of North Atlantic walrus taxonomy. Those
dastardly North Americans and Japanese! As it happens, this was nothing more than an unfortunate accident in word choice by Post (2004; see below) and difficulty in translating Dutch to English. Kohno and Ray (2008) humorously
responded to these comments:
“If Post’s
(2004:70) characterization of the study of Pliocene odobenines as complete
Babylonian confusion is correct, then he deserves some of the confusion for it.
He repeated previous generic misspellings, Trichechodon (p.70) and Obdobaenus
(p.73), in allusion to Trichecodon huxleyi Lankester, 1865. He
did not mention Alachtherium antwerpiensis Hasse, 1909, but did
attribute A. antverpiensis (Rutten, 1907) to Hasse, while not citing
Rutten at all, even though published in Amsterdam.
Although he noted (p.70) that even Americans and Japanese had meddled into
discussion of Pliocene walruses, he neglected to cite two of the most prominent
recent transgressions in support of his case…Our paper, based on Pliocene
fossils from the eastern United States,
may well be perceived as yet another transgression into European affairs. The
notorious disregard by marine mammals for political boundaries, though an
intractable problem in conservation, has made their fossils far more
interesting than would extreme provincialism. We do not share Post’s pessimism
about the status of knowledge of Pliocene walruses, but feel rather that much
progress has been made through the contributions of all who have focused on the
fossils, irrespective of nationality and in spite of multiplicity of
languages.”
UPDATE: I've been informed by a European colleague that the wording used by Post (2004) was accidental and not meant to convey any nationalistic issues, and instead was intended to simply express the variety of researchers from different regions weighing in on the taxonomy of Alachtherium. I've been informed that Kohno and Post get on quite well and have exchanged casts, and Post has even lived in Japan for a time. Thus it seems abundantly clear to me from my correspondence that no ill-will was intended and it was simply a case of "lost in translation". That all being said, lapses in citations and the like (as pointed out by Kohno and Ray, 2008) are arguably acceptable for a popular article. With this caveat, I've left the unedited quotations above.
The holotype of Pliopedia pacifica (left; latest Miocene Paso Robles Formation) and the referred forelimb and braincase (right; latest Miocene-earliest Pliocene Etchegoin Formation, California), from Kellogg (1921) and Repenning and Tedford (1977).
The Santa Margarita Walrus
In March 1909, Mr. Robert Anderson
found some large pinniped bones in a conglomerate about a mile southeast of the
dinky town of Santa Margarita in
the California coast ranges.
Later, this unit would later be named the Paso Robles Formation; in the
vicinity of Santa Margarita, it overlies the type section of the Santa
Margarita Sandstone, and is correlative in age with the Purisima Formation
(latest Miocene and Pliocene). The Paso Robles Formation was deposited on the
west side of the proto-coast ranges of California, which during the latest
Miocene formed a large island separating the Temblor Sea* to the east (where
the Etchegoin/San Joaquin Formations were deposited), which was connected to
the Pacific by a straight to the north (where the Purisima Formation was
deposited) and another straight to the south (where the Pismo Formation was
deposited). Pliopedia pacifica
was originally named from a fragmentary forelimb, which Kellogg (1922)
tentatively assigned to the Otariidae, but also recognized some walrus
features. Repenning and Tedford (1977) reported another partial skeleton
including a braincase, complete humerus, radius, and ulna from the Etchegoin
Formation (i.e. from within the Temblor
Sea). They curiously referred Pliopedia,
along with Valenictus imperialensis (keep reading) to the Dusignathinae,
despite correctly identifying that Pliopedia had an Odobenus-like
braincase and a deltoid tubercle separate from the deltopectoral crest of the
humerus. The braincase is similar to Odobenus, Alachtherium, and Valenictus
chulavistensis (see below) in lacking a sagittal crest and having a nuchal
crest expanded into a crescent-shaped muscle attachment surface. Barnes and
Raschke (1991) subsequently removed the Etchegoin Formation specimen from Pliopedia
and cited unpublished research on a toothless odobenine from the Purisima
Formation, which as of yet is still incomplete. Deméré (1994a) dismissed this
removal; I have reservations about why the specimen was removed, and I believe
that Repenning and Tedford (1977) were correct in their identification. Because
of the derive humeral and cranial morphology, Deméré (1994a) placed Pliopedia
within the Odobenini (see below) and indicated that more complete remains
would likely show that this walrus bore a pair of enlarged tusks. Pliopedia,
despite being poorly known (no additional material has been discovered since
the “pinniped bible” was published), demonstrates that a single species of
walrus inhabited both east and west shores of the coast range in the Pliocene.
I would absolutely love to conduct some fieldwork in the Kettleman Hills (type
section of Etchegoin and San Joaquin formations, along
the west side of I-5 in California
between Lost Hills and Kettleman City)
and search for additional walrus material.
*The Temblor Sea takes its name from the Temblor Range (or possibly the Temblor Formation, or perhaps both
are derived from the nearby Temblor Range). The Early Miocene age Pyramid Hill marine mammal
assemblage from the Jewett Sand and the middle Miocene Sharktooth Hill
assemblage from the Round Mountain Silt, both in the vicinity of Bakersfield, California, were deposited along the eastern shore of the Temblor Sea.
The holotype humerus of Valenictus imperialensis from the Pliocene Deguynos Formation of Imperial County, photographed at LACM.
Subtropical walruses? The Isla Cedros and Imperial
walruses
In 1961, Ed Mitchell named a new
genus and species of walrus from an isolated humerus collected from the early
Pliocene Imperial Group of southern California.
For the uninitiated, the Imperial Group is exposed in the Imperial desert near El
Centro, which is located just north of the US-Mexico
border, southwest of the Salton Sea, and east of San
Diego. The Imperial Group was deposited in a rapidly
subsiding basin and appears to have hosted a subtropical warm-water
invertebrate fauna, preserved within the proto-gulf of California.
The humerus was collected in 1949 from the Coyote
Mountains, and subsequent visits to
the locality by Ed Mitchell and others failed to yield any additional fossils;
in the subsequent 50 years, only a handful of additional bones have been
collected from the same formation. Mitchell (1961) correctly identified this
specimen as a walrus, and as such this fossil represented the first explicitly
recognized walrus from pre-Pleistocene rocks in the North Pacific. At the time,
the absence of pre-Pleistocene walrus remains in the region led other researchers
to propose that walruses immigrated to the Atlantic via
the Panama
seaway during the early Miocene. It seems a bit ridiculous now, but they really
were operating in a vacuum of information. Mitchell (1961) was thus the first
to identify that walruses did in fact have a North Pacific evolutionary
heritage, and suggested that a center of origin may yet be identified in the
North Pacific for walruses (as had already been identified for the Otariidae).
Mitchell also pointed out the rather robust and strange construction of the
humerus, including the huge knob-like medial entepicondyle, and suggested that Valenictus
had a powerful flipper stroke and probably did not swim in a manner similar to
otariids. The most interesting aspect of Valenictus imperialensis, aside from
its strange morphology, is that it – like Pliopedia – was found in
sediments deposited within a large embayment. Further making matters
interesting is that Repenning and Tedford (1977) reported a somewhat younger
partial humerus from the upper Pliocene San Joaquin Formation. The San Joaquin
Formation overlies the Etchegoin Formation in the Kettleman Hills, and marks
the final phase of marine sedimentation in the Temblor Sea; at the end of the
Pliocene, uplift of the Sierra Nevada caused a massive influx of sediment shed
westward into the San Joaquin Basin, which in concert with a Plio-Pleistocene
fall in sea level, caused the Temblor Sea to dry up, forming the modern day
southern San Joaquin valley. A last vestige of the Temblor
Sea is the shallow and freshwater Tulare
Lake west of Bakersfield,
which has been mostly emptied by 20th century irrigation. The San
Joaquin Formation is overlain by the estuarine and nonmarine uppermost Pliocene
and Pleistocene Tulare Formation (which is fossiliferous and has yielded
scrappy terrestrial mammals).
A few years later, a curious
pinniped was dug out of the badlands of the south end of Isla Cedros off the
Vizcaino Peninsula of Baja California by UC Riverside paleontology expeditions
led by paleontologist Frank Kilmer. They collected an enormous volume of
fossils which eventually led to the naming of various marine mammals like the
fur seal Thalassoleon mexicanus, the false killer whale Praekogia
cedrosensis, the porpoises Piscolithax boreios, Piscolithax
tedfordi, Albireo whistleri, and Parapontoporia pacifica, and
the early pilot whale-convergent beluga Denebola brachycephala. These
fossils came from deposits of the Almejas Formation – and the strange new
pinniped, despite lacking tusks, had several skull and postcranial features
that allied it with the modern walrus – and Repenning and Tedford (1977) named
it Aivukus cedrosensis (the genus name is Inuit for ‘walrus’). Aivukus
has an elongate rostrum, small canines, highly worn teeth, reduced incisors,
but an Odobenus-like basicranium and postcrania. The mandible of Aivukus
was thought to have some similarities with Prorosmarus alleni, leading
Repenning and Tedford (1977) to hypothesize that it was directly ancestral to Prorosmarus.
Aivukus represents the most southerly described walrus, at about 28˚
latitude, and like Valenictus imperialensis, demonstrates that walruses
inhabited subtropical waters. The southern occurrence of Aivukus led
Repenning and Tedford (1977) to hypothesize that it or something similar immigrated
to the Atlantic via the still-open Panamanian Seaway to
give rise to Prorosmarus, Alachtherium, and eventually Odobenus
during the Pliocene and Pleistocene.
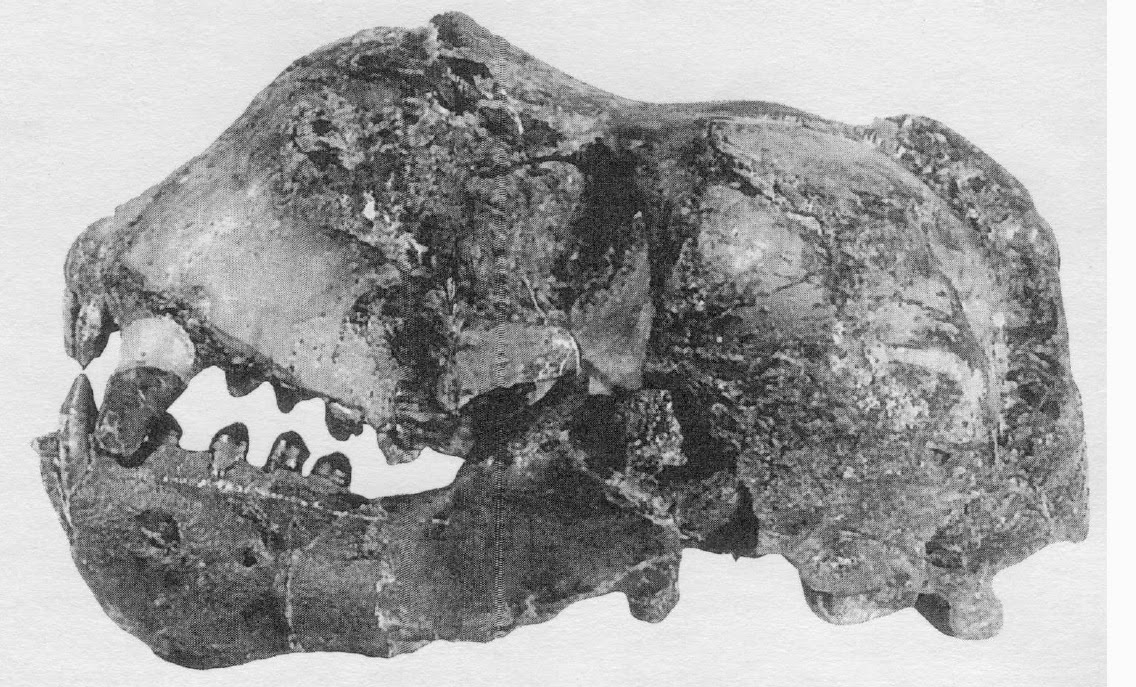
Cast of the holotype skull of Aivukus cedrosensis from the late Miocene Almejas Formation of Baja California, photographed at the USNM.
The toothless Chula Vista walrus and a makeover of Valenictus
In the late 1980’s more discoveries
were being made in the hills around San Diego, California.
The Pliocene San Diego Formation had long been known to host a magnificent
invertebrate fossil assemblage but had also produced a fair number of birds
including several species of the flightless auk Mancalla, the fur seal Callorhinus
gilmorei, the longirostrine dolphin Parapontoporia sternbergi,
and baleen whales like Balaenoptera davidsonii. Subdivision-scale
housing construction was booming in the 1980’s, and these construction
operations often scraped off bedrock, uncovering vertebrate fossils in the
process. Paleontological mitigation began in Orange
County in the 1970’s and San
Diego followed shortly thereafter (I’m not exactly
sure on the timing of mitigation in San Diego
or LA county, to be perfectly honest). This led to a figurative explosion in
the amount of fossil vertebrates collected, and now institutions housing
mitigation-derived collections like the Natural History Museum of LA, the San
Diego Natural History Museum, and (most significantly) the Cooper Center are
packed to the brim with exciting collections of marine vertebrates (99% of
which are undescribed!).
The holotype skull of Valenictus chulavistensis (Pliocene, San Diego Formation, California), photographed at the SDNHM.
Valenictus chulavistensis
was one of those discoveries. A couple of tusks from the San Diego Formation
were originally thought to represent some sort of weird proboscidean; a
strange, toothless mandible found later yielded no further clues. A partial
skeleton was subsequently discovered, including a fragmentary odobenine walrus
skull with the same type of tusk, a humerus with the same strange morphology as
Valenictus imperialensis, and the strange mandible, as well as a bunch
of other postcranial bones – confirming that Valenictus imperialensis was
indeed a tusked odobenine walrus (Deméré 1994b). Weirder yet, the mandible and
skull lacked any teeth aside from the upper canine. A nearly complete but
smaller (and therefore younger) male skull was found and designated as the
paratype for the species; this second skull, along with an isolated juvenile
maxilla, demonstrated that the lack of teeth in the adult holotype specimen was
not some weird pathologic condition. Since the early 90’s, four additional
skulls have been found, and none of them exhibit any non-canine teeth.
The more completely preserved paratype skull of Valenictus chulavistensis; this is the skull figured in Demere (1994b).
Deméré (1994b) explained that
studies of walrus feeding show that modern walruses do not use their teeth
during feeding, and rather only clack their teeth together as a form of
underwater communication. The classic study of walrus biology and behavior by
Francis Fay (1982) examined feeding behavior and showed that walruses have a
powerful ability to generate oral suction by using their tongue as a piston
against the deeply vaulted palate. The poor defenseless clam, after being
unearthed (typically by water jetting, using the opposite of suction; walruses
do not use their tusks for “digging”) is manipulated into place by the walrus’
fleshy lips, and the suction generated is sufficient enough to suck the soft
tissues right off of the shell (other observations by Fay included a walrus
feeding on a small phocid seal it had presumably killed, and was just sucking
the flesh right off of the bone). Valenictus chulavistensis shares a
vaulted palate and was just as well-adapted for suction feeding as Odobenus.
Tooth loss in Valenictus is therefore analogous to tooth loss in
suction-feeding beaked whales, and is a remarkably derived condition amongst
pinnipeds. In fact, it’s also worth pointing out that Odobenus is
evolving towards tooth loss: it’s already lost its medial incisors, the fourth
premolar, and upper and lower molars.
The holotype mandible of Valenictus chulavistensis...
Another curious feature is the
highly dense, pachyosteosclerotic nature of the postcranial bones. The bones
have a reduced medullary zone (osteosclerosis) and inflated proportions and
cortex relative to other pinnipeds (pachyostosis). Modern Odobenus bones
are slightly denser than other pinnipeds, and the skull in particular is
extraordinarily dense – but the postcrania of Valenictus are massive,
dense, and very heavy (and not just because of fossilization). SDNHM visits can
actually be sort of a pain if I’m interested in photographing Valenictus bones
because they’re so damn heavy (but chicken scratch compared to baleen whales,
I’ll add). Dense bones are thought to act as ballast, and the denser bones of Valenictus
suggests it had a unique ecology with respect to other odobenines. Valenictus
is known from the proto-gulf of California,
the Temblor Sea
(Deméré, 1994a,b actually reidentified the San Joaquin Fm. specimen as a
specimen of V. chulavistensis), and the Pliocene San Diego embayment,
and was a benthic feeder. Deméré (1994b) suggested that benthic feeding in
relatively warm waters would have favored increased bone ballast. Barnes (2005)
preliminarily reported additional pachyosteosclerotic Valenictus
occurrences from southern Baja California,
and suggested that the hypersaline environments in some of these embayments would
have also fostered adaptations towards overcoming greater buoyancy. Finally, some
new specimens from the Purisima Formation near Santa Cruz
include a femur and a complete skull (collected recently by high school student
and avid amateur paleontologist Forrest Sheperd), both identifiable as Valenictus
– demonstrate that Valenictus also existed somewhat further north at the
terminus of the northern connection of the Temblor
Sea.
...And the holotype humerus of Valenictus chulavistensis, photographed at the SDNHM. Note the similarities with Valenictus imperialensis (above).
Deméré (1994a) also conducted the
first phylogenetic analysis of walruses, as I’ve alluded to in earlier posts.
This analysis confirmed the monophyly of the Odobeninae, and recovered Aivukus
as the earliest diverging odobenine. Alachtherium was the next diverging
odobenine, which in turn was sister to an Odobenus + Valenictus
clade. Demere (1994a) importantly noted that amongst walruses, only Alachtheirum, Valenictus, and Odobenus possessed globular dentine, and named the tribe Odobenini to unite the long-tusked odobenines together. In a phylogenetic and morphological context, Deméré (1994a) argued that Valenictus
is actually more derived than the extant walrus Odobenus rosmarus
– and certainly, given details of the dentition and postcranial skeleton, he
makes an excellent case. For whatever reason, Valenictus went extinct at
the end of the Pliocene. If you want to read up more on that, I wrote a bit
about Plio-Pleistocene marine mammal extinctions in my recent Geodiversitas monograph
(Boessenecker, 2013).
One last Valenictus chulavistensis - a composite skeleton (all San Diego Formation material) on display at the SDNHM; the paratype skull can be seen upside-down behind the skeleton.
More records of the Odobeninae from Japan
Another important Pliocene
odobenine was published in the 1995 special volume of The Island Arc by Hideo
Horikawa, in which he named the small, primitive odobenine Protodobenus
japonicus. Protodobenus lacks tusklike canines, and it is unclear if
it possessed globular dentine. It did on the other hand possess an
Odobenini-like deep, robust rostrum, and retained the primitive number of
teeth. Protodobenus lacked extreme dental wear and also had a flattish
palate, suggesting it was incapable of effective suction feeding and likely
subsisted on fish. In this context, it’s unclear why it evolved such a deep
rostrum; damage to the skull shows that the canines have elongate roots, and in
the Odobenini, the inflated rostrum accommodates the enormous canine roots.
More on this in the next post…
An important contribution towards
the evolutionary history of odobenines was published by Kohno et al. (1995),
who reported several tusks from the Pliocene of Japan. Following the definition
of Deméré (1994), they identified a number of tusks with globular dentine from
lower and upper Pliocene localities in Japan,
which they identified to the tribe Odobenini. Most of these have an oval-shaped
cross section, are more highly curved and tapering than Odobenus rosmarus,
and some possess longitudinal fluting – and therefore compare well with tusks
of the Alachtherium-Ontocetus-Prorosmarus-Trichecodon
morphotype (see below). Critically, they identified a single tusk of Odobenus
sp. from the upper Pliocene (see section on Odobenus for more on this). The
importance here is that, based on tusks, a minimum of two species of Odobenini
appear to have coexisted in Japan
during the Pliocene.
The skull and mandible of Protodobenus japonicus - the first deep-snouted walrus, from the early Pliocene of Japan.
The first record of Alachtherium from outside the North Atlantic: a skull of Alachtherium sp. from the early Pliocene of Japan. From Kohno et al. (1998).
Alachtherium from Japan…
and Africa?!
A couple of surprising occurrences
of the Pliocene walrus Alachtherium were reported in the late 1990’s. In
1997, Denis Geraads (who specializes in African mammal paleontology) described
a new species of Alachtherium from the upper Pliocene of Morocco, based
on a fragmentary skull, a partial mandible, and a partial humerus. Although the
species is founded upon material that is of dubious diagnostic value, it clearly
represented Alachtherium and nonetheless demonstrates that walruses
formerly inhabited the northwestern shoreline of Africa.
The following year, Kohno et al.
(1998) described a fantastically preserved skull from the early Pliocene of
Japan they identified as Alachtherium sp. This skull doesn’t quite have
the rectangular outline in posterior view like Alachtherium cretsii, but
has a similarly short, curved tusk with an oval cross section, a slightly
longer rostrum, and a full complement of postcanine teeth (preserved only as
alveoli, unfortunately). This discovery indicates that Alachtherium was
present in both the Atlantic and Pacific during the
Pliocene, and likely used the Arctic portal as a means for dispersal, which had
recently opened up at 5 Ma (Marincovich, 2000; see below).
The referred humeri, tibia, and mandible of Alachtherium africanus, from Geraads (1997).
The Lee Creek walruses and a taxonomic solution for Alachtherium
Various researchers including Deméré
(1994a), Post (2004), and Kohno and Ray (2008) have preferred a single species
assignment for North Atlantic walrus remains. In fact,
although using a weird taxonomy, Erdbrink and Van Bree (1999) also preferred a
single species, “Odobenus antverpiensis”, which others (Deméré, 1994a;
Kohno and Ray, 2008) cogently argued was clearly a junior synonym of Alachtherium
cretsii.
In 2008, Naoki Kohno and Clayton
Ray published their monograph of walrus remains from the Pliocene Yorktown
Formation in the long-awaited Lee Creek IV volume (seriously, if you’re
interested in marine mammals from the east coast, do yourself a favor and buy a
copy through the Virginia Museum of Natural History). First, they laid out all
the prior taxonomic arguments, which are summarized here in bullet format for
convenience:
-Ontocetus emmonsi is a Pliocene walrus from the
Yorktown Formation, originally named as a cetacean in 1859 by Joseph Leidy,
based on a partial tusk
-Trichecodon huxleyi from the upper Pliocene Red Crag
(UK), named in 1865 by Lankester, was based on an isolated tusk similar to Ontocetus
emmonsi
-Alachtherium cretsii named by Du Bus (1867) from
lower Pliocene Scaldisian sands of Belgium
based on well-preserved mandible
-Trichechodon koninckii was named from a fragmentary
tusks by Van Beneden (1871), also from the lower Pliocene Scaldisian sands of Belgium,
later identified by many later authors as non-diagnostic and a nomen nudum
or nomen dubium
-Prorosmarus alleni named from incomplete mandible
from Yorktown Fm. by Berry and
Gregory (1906)
-Trichechus antverpiensis erected by Rutten (1907)
for partial skull originally referred to A. cretsii by Van Beneden (1877)
-Alachtherium antwerpiensis named by Hasse (1910) for
other cranial material from Pliocene of Belgium
-Trichechus antverpiensis recombined as Odobenus
antverpiensis by Van der Feen (1968), followed by Erdbrink and Van Bree
(1986, 1990, 1999)
-T./O. antverpiensis and Alachtherium antwerpiensis
synonymized with Alachtherium cretsii by Deméré (1994a), followed
by Post (2004)
-Alachtherium africanus named by Geraads (1997) from
fragmentary cranial elements from the Pliocene of Morocco
The holotype tusk fragment of Ontocetus emmonsi - and the "parent" specimen of virtually all North Atlantic Pliocene walruses (=Alachtherium cretsii, Alachtherium antwerpiensis, Trichecodon huxleyi, Trichecodon/Odobenus antverpiensis, Prorosmarus alleni), photographed at the USNM.
Kohno and Ray (2008) further
considered Prorosmarus alleni to be relatively similar to the type
mandible of A. cretsii, and figured a new mandible that is intermediate
between the two, indicating that the perceived absence of an upturned symphysis
is probably an ontogenetic feature. They also pointed out that the holotype
tusk of Ontocetus emmonsi is a walrus, and that it and the
holotype tusk of Trichecodon huxleyi both share an oval, transversely
compressed cross section, longitudinal fluting, greater curvature, and are more
tapered in contrast to the more elongate, straighter, smoother tusks of Odobenus
rosmarus, which also have more of a circular cross section. Most
significantly, they identify that all tusks found in sediments of Pliocene age
yielding remains of Alachtherium/Trichecodon/Prorosmarus
all conform to this morphology. They showed some bivariate plots of Atlantic
Pliocene walrus tusks, and showed conclusively that all of these tusks conform
to similar proportions, and cluster together to the exclusion of Odobenus
rosmarus (Kohno and Ray 2008: fig. 27). In light of this information,
they synonymized all Pliocene Atlantic walruses with Ontocetus emmonsi.
An adorable Ontocetus emmonsi juvenile maxilla (complete with mini-tusk!) from the Pliocene Yorktown Formation, described and figured by Kohno and Ray (2008), photographed at the USNM. Seriously, that is a cute fossil.
It’s admittedly a controversial
decision, and some other pinniped workers have expressed the notion that Alachtherium
cretsii is a better name as it is founded upon a complete mandible that
inherently preserves more morphological information and is thus certainly more
diagnostic than a tusk. I’m on the fence; on one hand, if the tusk morphology
proves in the long run to really be that distinctive (and so far, it seems to),
then Ontocetus emmonsi works; on the other hand, an isolated fragmentary
tusk may not be diagnostic and in cetacean paleontology most species named off
of isolated teeth were shit-canned a long time ago. My mind isn’t completely
made up, and I think both camps in favor of Ontocetus emmonsi or Alachtherium
cretsii have decent arguments.
The fossil record and biogeography of Odobenus
Pleistocene fossils of the modern
walrus Odobenus have been widely reported from coastlines and the sea
floor from both sides of the North Pacific (e.g. California,
British Columbia, Japan)
and North Atlantic (Maritime
provinces of Canada,
eastern USA – New
Jersey to Georgia,
and the UK and Netherlands)
as well as the Arctic (Canada).
Historically, many of the Pleistocene tusks, crania, mandibles, and other
remains were assigned to Trichecodon huxleyi by earlier workers (e.g.
Rutten, 1907); Demere (1994a) recombined it as Odobenus huxleyi, remarking that it was possibly diagnosable based on possessing a thin cementum layer in the holotype tusk; however, Kohno and Ray (2008) indicated that the tusk is identical to Ontocetus emmonsi (regardless, most material referred to T. huxleyi does appear to represent Odobenus rather than Alachtherium/Ontocetus). Fossils assignable to the extant genus Odobenus are
widely reported from Pleistocene deposits in the Northern Hemisphere; in North
America, fossils of Odobenus rosmarus have been dredged
from as far south as the San Francisco
Bay in California
(Harington, 1984) and Georgia
(Sanders 2002). These southerly records likely reflect southward latitudinal
expansion of the natural range of Odobenus rosmarus during cold glacial
periods. Furthermore, trace fossil evidence has recently been identified from
the Olympic Peninsula in Washington, USA,
indicating the presence of suction/jet-feeding walruses during the late
Pleistocene (Gingras et al. 2007).
A Pleistocene skull figured and referred to Odobenus huxleyi (=Odobenus rosmarus), and the braincase of Alachtherium cretsii/Ontocetus emmonsi named as the new species Trichecodon antverpiensis by Rutten (1907).
That’s all neat, but not very
surprising: modern Odobenus rosmarus is predominantly Arctic in
distribution but occurs at the fringes of the North Pacific and extensively in
the Northernmost Atlantic, and we know it was pretty damn cold during parts of
the Pleistocene, facilitating southward migration during cold periods. But how
old is the Odobenus lineage? And where the hell did it come from?
Cross-sections of Pleistocene and modern Odobenus tusks, with the illustration of the broken cross-section of the type specimen of Hemicaulodon effodiens, a junior synonym of Odobenus rosmarus. From Ray (1975). Note the distinctive core of globular dentine. This is a typical record of isolated Odobenus tusks from Pleistocene sediments.
At the time of writing the pinniped bible, Repenning and
Tedford (1977) were sort of at a loss for the more recent evolutionary history
of the modern walrus. Most of the remains were Pleistocene in age, and more or
less confined to the above described regions: mostly in the North
Atlantic and fringes of the Arctic. Based
upon their discovery of the tuskless odobenine Aivukus cedrosensis
from Baja California (which they also presumed was phylogenetically close to Prorosmarus
alleni based on mandibular similarities; of course we now know that Aivukus
and “Prorosmarus” had widely disparate skull morphology), they
hypothesized that the ancestor of all tusked walruses (=Odobenini of modern
usage) dispersed to the North Atlantic prior to the closure of the Panamanian
isthmus. Following this, the extant Pacific walrus (Odobenus rosmarus
divergens) reinvaded the northernmost Pacific late in the Pleistocene. This
hypothesis began to unravel upon the discovery of tusked walruses like Valenictus
chulavistensis from California (confirming that the genus Valenictus
was assignable to the Odobenini rather than Dusignathinae), Protodobenus
from Japan, and another toothless walrus from the Purisima Formation of
California, all indicating that tusked walruses persisted in the North Pacific
long after the disappearance of Aivukus (Kohno et al., 1995). A new
extinct species of Odobenus was named by Tomida (1989) which he named Odobenus
mandanoensis, from the middle Pleistocene of Japan. It proportionally
differs from extant Odobenus and appears to have been slightly larger;
although fragmentary, it appears to genuinely reflect a separate species
(Deméré, 1994a).
An isolated tusk fragment from the Purisima Formation (this specimen may be seen on display at the Santa Cruz Museum of Natural History), with globular dentine; the distinctive dental tissue identifies this tusk to the Odobenini. This and another specimen are from approximately the Miocene-Pliocene boundary, and therefore constitute some of the oldest records of the Odobenini.
One of the most fascinating
advances was the discovery tusks and crania assignable to Odobenus from
the upper Pliocene of Japan. Aside from the aforementioned tusk described by
Kohno et al. (1995), a nearly complete skull of Odobenus sp. with tusk
dredged from the Sea of Okhotsk
was reported by Miyazaki et al. (1992), who found that it was associated with
late Pliocene microfossils. These finds indicate that while Valenictus was
hanging out in warm waters along the California
and Baja California margin, and
while Ontocetus/Alachtherium was proliferating across virtually
the entire North Atlantic, the modern walrus had already
evolved in the western North Pacific.
The curious referred mandible of Odobenus "koninckii", identified here as Odobenus sp., from the Pliocene Scaldisian Sands of Belgium, from Van Beneden (1877).
A single commonly overlooked fossil
from the early Pliocene of Belgium indicates that perhaps neither of these two
possibilities are likely. Although the name Trichechodon koninckii
is defunct and useless, a single mandible apparently from the Pliocene
Scaldisian sands of Belgium
referred to T. koninckii and figured by Van Beneden (1877) bears a
non-upturned symphyseal region and a fused symphysis, two features unique
(amongst the Odobenini) to Odobenus. Deméré (1994a) pointed out that
this specimen reflects a primitive Odobenus that retains a fourth lower
premolar, a canine that is slightly larger than the premolars, as well as a
sinuous outline of the mandible in dorsal view; the specimen is of apparent
Pliocene age, and appears to indicate that Odobenus can be tracked to the early
Pliocene in the North Atlantic, a bit older than the late Pliocene of the
western North Pacific. What could this suggest? Perhaps it suggests a third
option, that ancestral Odobenus had, like today, a circum Arctic
distribution that extended as far south as Japan and Belgium during the
Pliocene, facilitated by the lack of extensive ice sheets. Such a distribution
may have pre-adapted Odobenus for Pleistocene glaciation. It’s possible,
but other hypotheses are equally likely, and we need more walrus fossils with
better dates to get a more complete picture.
Whatever happened, we know the
following take-home points: 1) until the Pleistocene, tusked walruses
(Odobenini) enjoyed a much wider variety of habitats and happily existed as far
south as Baja California, Florida, and Morocco, and Pliocene fossils of the
genus Odobenus are found at latitudes that would have been temperate
during the Pliocene; 2) Sometime during the past 2 million years, a lineage
within the genus Odobenus transformed from a temperate species (as was
typical of Pliocene Odobenini) into the Arctic glacially-adapted specialist we
know today.
The diversity of tusked walruses (Odobeninae); note the much smaller size of Aivukus and Protodobenus, and the gigantic size of Ontocetus emmonsi/Alachtherium cretsii.
References
L.G. Barnes. 2005. Dense boned late Miocene and Pliocene fossil walruses of the Imperial Desert and Baja California: possible buoyancy-control mechanisms for feeding on benthic marine invertebrates in the proto-Gulf of California. Abstracts of Proceedings, 2005 Desert Symposium.
E. W. Berry and W. K. Gregory. 1906. Prorosmarus alleni, a new genus and
species of walrus from the upper Miocene of Yorktown, Virginia. American Journal of Science 21:444-450
R.W. Boessenecker. 2013. A new marine vertebrate assemblage from the late Neogene Purisima Formation in Central California, part II: pinnipeds and cetaceans. Geodiversitas 35:815-940.
T. A. Demere. 1994a. The Family Odobenidae: A phylogenetic analysis of fossil and living taxa. Proceedings of the San Diego Society of Natural History 29:99-123
T. A. Demere. 1994b. Two new species of fossil walruses (Pinnipedia: Odobenidae) from the upper Pliocene San Diego Formation. Proceedings of the San Diego Society of Natural History 29:77-98
B. Du Bus. 1867. Sure quelques mammiferes du Crag d'Anvers. Bulletin de l'Academie royale des sciences, des lettres et des beaux-arts de Belgique 24:562-577.
D. P. B. Erdbrink and P. J. H. Van Bree. 1986. Fossil Odobenidae in some Dutch collections (Mammalia, Carnivora). Beaufortia 36(2):13-33
D. P. B. Erdbrink and P. J. H. Van Bree. 1990. Further observations on fossil and subfossil odobenid material (Mammalia, Carnivora) from the North Sea. Beaufortia 40(5):85-101.
D. P. B. Erdbrink and P. J. H. Van Bree. 1986. Fossil cranial walrus material from the North Sea and estuary of the Schelde (Mammalia, Carnivora). Beaufortia 49(1):1-9
D. Geraads. 1997. Carnivores du Pliocene terminal de Ahl al Oughlam (Casablanca, Maroc). Géobios 30(1):127-164
M. K. Gingras, I.A. Armitage, S.G. Pemberton, and H.E. Clifton. 2007. Pleistocene walrus herds in the Olympic Peninsula area: trace-fossil evidence of predation by hydraulic jetting. Palaios 22:539-545.
C. R. Harington. 1984. Quaternary marine and land mammals and their paleoenvironmental implications - examples from Northern North America. Special publication of the Carnegie Museum of Natural History 8:511-525.
G. Hasse. 1909. Les Morses Pliocene poederlien a Anvers. Bulletin de la Societe Belge de Geologie de Paleontologie et D'Hydrologie (Bruxelles) 23:293-322
H. Horikawa. 1995. A primitive odobenine walrus of Early Pliocene age from Japan. The Island Arc 3:309-328
R. Kellogg. 1922. Pinnipeds from Miocene and Pleistocene deposits of California. University of California Publications in Geological Sciences 13(4):23-132
N. Kohno and C. E. Ray. 2008. Pliocene walruses from the Yorktown
Formation of Virginia and North Carolina, and a systematic revision of
the North Atlantic Pliocene walruses. Virginia Museum of Natural History Special Publication 14:39-80
N. Kohno, K. Narita, and H. Koike. 1998. An early Pliocene odobenid (Mammalia: Carnivora) from the Joshita Formation, Nagano Prefecture, central Japan. Research Reports of the Shinshushinmachi Fossil Museum 1:1-7.
N. Kohno, Y. Tomida, Y. Hasegawa, and H. Furusawa. 1995. Pliocene tusked odobenids (Mammalia: Carnivora) in the western North Pacific, and their paleobiogeography. Bulletin of the National Science Museum 21:111-131.
E. R. Lankester. 1865. On the sources of the mammalian fossils of the
Red Crag, and the discovery of a new mammal in that deposit, allied to
the walrus. Quarterly Journal of the Geological Society of London 21:221-232
J. Leidy. 1859. [Remarks on Dromatherium sylvestre and Ontocetus emmonsi]. Proceedings of the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia 1859:162
L. Marincovich. 2000. Central American paleogeography controlled Pliocene Arctic Ocean molluscan migrations. Geology 28:551-554.
E. D. Mitchell. 1961. A new walrus from the imperial Pliocene of
Southern California: with notes on odobenid and otariid humeri. Los Angeles County Museum Contributions in Science 44:1-28
S. Miyazaki, M. Kimura, and H. Ishiguri. 1992. On a Pliocene walrus (Odobenus sp.) discovered in the northern Pacific Ocean. Journal of the Geological Society of Japan 98:723-740.
K. Post. 2004. What's in a name: Alachtherium cretsii, de Pliocene van de Nordzee. Grundboor & Hammer 58:70-74.
C. E. Ray. 1975. The relationshiops of Hemicaulodon effodiens Cope 1869 (Mammalia; Odobenidae). Proceedings of the Biological Society of Washington 88(26):282-304
C. A. Repenning and R. H. Tedford. 1977. Otarioid seals of the Neogene. Geological Survey Professional Paper 992:1-93
L. Rutten. 1907. On fossil trichechids from Zeeland and Belgium. Proceedings of the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences 10(1):2-14
A.E. Sanders. 2002. Additions to the Pleistocene mammal faunas of South Carolina, North Carolina, and Georgia. Transactions of the American Philosophical Society 92:1-152.
P.J. Van Beneden. 1871. Les phoques de la mer Scaldisienne. Bulletin du Academie Royale de Belgique 32:5-19.
P.J. Van Beneden. 1877. Description des ossements fossiles des environs d'Anvers. Annales du Musee Royal d'Histoire Naturelle de Belgique, Tome 1. Premiere Partie, Pinnipedes ou Amphitheriens: 1-88.
P.J. Van der Feen. 1968. A fossil skull fragment of a walrus from the mouth of the river Scheldt (Netherlands). Bijdragen tot de dierkunde 38:23-30.