Read Part 1 here for an introduction to whale and dolphin earbones (recommended before diving right in).
This is perhaps the part that most readers are looking for – how to identify different dolphin periotic bones. For each family of cetaceans, I’ll briefly list the approximate size reported as complete periotic length (not specific measurements, this is from memory), some of the main attributes, along with any unique features of the family or higher level features within Odontoceti, similar periotic morphs they can be confused with, age, known distribution, and established localities (e.g. localities, including rock unit, where these are confirmed to have been found or are reliably known from).
This guide is not exhaustive, nor is it perfect: identifying isolated periotics has long been called a 'black art' even by seasoned whaleontologists. The attributes listed below should not be interpreted by professionals as synapomorphies - they are generalizations, which can help someone identify many isolated periotics to the family level. Some families are very obvious, but others range quite a bit in anatomy, overlapping with other families - this is particularly a problem within the Delphinoidea. Regardless, I have almost certainly glossed over some important details and missed some things - so if you want to help me improve this, let me know what I've screwed up! Also, I will likely expand this in the future. The specimens in this post are mostly in collections of the Mace Brown Museum of Natural History; genus-level identifications (upper right) for some of these should be taken with a grain of salt. All photographs are by me, unless otherwise stated.
Though many features and conditions vary considerably and have evolved and lost again and again, some major groups are united by some periotic features. Archaic dolphins generally have long anterior and posterior processes and some remnant of the suprameatal fossa, which is large and deep in basilosaurid whales. Many archaic dolphins, as well as platanistoids, have a small spur lateral to the posterior process called the articular process - in Platanista (Ganges river dolphin) it is long and hooked, and generally needs to be broken in order for the periotic to be removed from the skull. The anterior bullar facet is primitively shallow in the earliest dolphins, but deeply concave in many long-snouted early to middle Miocene dolphins (Eurhinodelphinidae, Eoplatanistidae), and the facet is lost entirely in Delphinoidea. Delphinoids also tend to have a proportionally huge pars cochlearis.
As with all other fossils, periotic bones have some degree of natural variation. Above are some photos of periotics of Parapontoporia sternbergi, reasonably interpreted by L.G. Barnes (1985) as a single species from the San Diego Formation of southern California (Pliocene). You'll notice that much of the variation is in the length and inflation of the anterior process and the particular shape of the posterior bullar facet. The cochlear morphology - especially ventrally - seems to vary the least, which according to my Ph.D. adviser Ewan Fordyce, is likely because it ossifies the earliest and is associated with the middle ear sinus. The dorsal side varies considerably as this continues to ossify during growth, so the shape and size of the body and the configuration of foramina and crests within the meatus, and the shape and size of the meatus itself, also can change during growth. What this means is that no two periotics of the same species will ever be identical, and I guarantee you will go mad picking out differences between specimens only to find out they represent different edges of the anatomical envelope of variation or juveniles v. adults. As a result, it's better to look for shared similarities and when possible, match a particular periotic morph to periotics found associated with a skull, though this is certainly more typically the realm of activities of a whaleontologist rather than an amateur collector as many such specimens needed for such comparisons are in museum collections. Image from Barnes (1985).
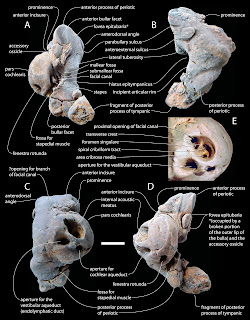
And, just for reference, here is the complete labeled figure of the periotic of a bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus) from Mead and Fordyce (2009).
Xenorophidae
Size: Small (~2.5-4 cm)
Attributes: Anterior process short and typically ‘hatchet’ shaped or rectangular in medial view, with bladelike tip in ventral view; pars cochlearis large, boxy; low superior process present, along with a suprameatal fossa (a deep, small, circular pit in some), short posterior bullar facet, long, triangular lateral tuberosity. Anterior process bears shallow anterior bullar facet and often is hatchet shaped or rectangular in medial view. A small to medium articular process may be present anterolateral to the posterior process.
Confused with: Difficult to confuse these with other odontocetes, perhaps agorophiid periotics.
Typically found genera: Albertocetus, Echovenator, Xenorophus
Age: Oligocene
Distribution: South Carolina (mostly), some specimens from North Carolina
Established Localities: Ashley and Chandler Bridge formations, Charleston, South Carolina.
Abundance: Uncommon in Charleston, South Carolina.
Simocetidae
Size: Small (~2.5-4 cm)
Attributes: Long subrectangular anterior process with bladelike anterior tip (in medial view), broad shallow suprameatal fossa with low, rounded superior process lateral to it, triangular and bladelike lateral tuberosity, dorsoventrally shallow pars cochlearis frequently with anteromedial bony spurs giving it a subrectangular shape, transversely narrow and dorsomedially facing internal acoustic meatus, low articular process, ventrally deflected posterior process with flat to sinuous smooth to grooved and leaf-shaped posterior bullar facet.
Confused with: Perhaps Xenorophidae and Waipatiidae.
Typically found genera: none are ‘typically’ found, but some named simocetid-grade dolphins from the Pacific Northwest include Simocetus and Olympicetus.
Age: Oligocene
Distribution: North Pacific.
Established Localities: Alsea Formation, Oregon; Pysht Formation, Washington.
Abundance: Rare, but Olympicetus is locally common in
the Pysht Formation.
Agorophiidae
Size: Medium to large (3-5cm).
Attributes: Elongate periotics with long anterior and posterior processes, anterior process lozenge-shaped with blunt apex, and shallow anterior bullar facet; trough-like suprameatal fossa, small, hemispherical pars cochlearis, long and tapering posterior bullar facet with deep grooves at very end but otherwise flat. Periotics of Ankylorhiza are large with dorsally expanded and slightly flattened anterior process that is triangular and somewhat ventrally deflected in medial view; posterior bullar facet is proportionally smaller.
Confused with: Waipatiidae, Squalodontidae. Squalodontids possess a large tubercle on the medial side of the anterior process and a posterior bullar facet that is ‘folded over’ into two facets, rather than the flat facet in Agorophiidae. Periotics of the giant dolphin Ankylorhiza in particular can be confused with Squalodon.
Typically found genera: Agorophius, Ankylorhiza
Age: Oligocene.
Distribution: North Atlantic and Paratethys (eastern Europe).
Established Localities: Ashley and Chandler Bridge Formations of South Carolina.
Abundance: Locally common in Charleston, South Carolina.
Waipatiidae
Size: medium (~3-4 cm)
Attributes: Periotics with long, cylindrical anterior processes (with shallow to moderately deep anterior bullar facet) that are generally not bent medially or ventrally with triangular shape in medial view, small hemispherical pars cochlearis, bump-like lateral tuberosity, a suprameatal fossa developed as a sulcus or furrow, and medium to long posterior processes that can be ventrally deflected. A small articular process may be present anterolateral to the posterior process. Often has U or C-shaped parabullary sulcus on lateral side of anterior process.
Confused with: Squalodontidae, Agorophiidae. Very similar to the latter, differs from former in smaller size and by (typically) lacking a tubercle on medial side of anterior process.
Typically found genera: Waipatia, Ediscetus, Otekaikea; many unnamed taxa from Charleston, SC
Age: Oligocene, earliest Miocene.
Distribution: New Zealand, North Atlantic, Mediterranean, Paratethys?
Established Localities: Oligocene Kokoamu Greensand and Otekaike Limestone of New Zealand, with some likely (but unpublished) waipatiids from the Ashley and Chandler Bridge formations of South Carolina.
Abundance: Common in Charleston, South Carolina, and
Oligocene of New Zealand.
Squalodontidae
Size: Medium to large (3.5-5 cm).
Attributes: Long, robust anterior process with shallow anterior bullar facet and process with a triangular apex in medial view; massive body lacking suprameatal fossa or superior ridge, and lateral surface transversely expanded, often with oblique striations, proportionally small and hemispherical pars cochlearis, internal acoustic meatus usually transversely narrow, large tubercle present on medial side of anterior process, and posterior bullar facet folded over into two surfaces at approximately a 90 degree angle; hinge of posterior bullar facet transitions into posteriorly elongate apex of posterior process. A small articular process may be present anterolateral to the posterior process.
Confused with: Waipatiidae, Agorophiidae.
Typically found genera: Eosqualodon, Squalodon
Age: latest Oligocene?, mostly early to middle Miocene.
Distribution: Worldwide.
Established Localities: Calvert Formation, Maryland/Virginia; Pungo River Limestone, North Carolina; Belluno Sandstone, Italy.
Abundance: Uncommon.
?Yorktown Formation or Pungo River Limestone, Mio-Pliocene, Lee Creek Mine, North Carolina, USA, CCNHM collections.
Physeteridae
Size: Medium to Large (3-5+ cm)
Attributes: Proportionally small, ventrally curving anterior process; proportionally enormous pars cochlearis; internal acoustic meatus is frequently narrow, keyhole-shaped and transversely oriented rather than oblique or anteroposteriorly; massive, hemispherical lateral tuberosity; meatus lacks transverse crest; body of periotic dorsoventrally deep and frequently bears triangular peak (dorsal and posterior margins forming a corner); large accessory ossicle frequently fused to anterior process.
Confused with: Kogiidae, perhaps Ziphiidae.
Typically found genera: Aulophyseter, Orycterocetus.
Age: early Miocene to Pliocene (recent).
Distribution: Worldwide.
Established Localities: Calvert Formation, Maryland/Virginia; Sharktooth Hill, California.
Abundance: Rare.
Both from Yorktown Formation, Pliocene, Lee Creek Mine, North Carolina, USA, CCNHM collections.Kogiidae
Size: Small to Large (2-4.5 cm)
Attributes: Anteromedially directed anterior process with rectangular outline in ventral and medial view, anterior process often bilobate with sulcus dividing it into dorsal and ventral partitions; accessory ossicle often fused in place; transversely oriented internal acoustic meatus like Physeteridae, crista transversa occasionally elevated; pars cochlearis small and somewhat anteroposteriorly compressed with fenestra rotundum; small lateral tuberosity; large to enormous posterior bullar facet with flat posterior bullar facet that is posteriorly flattened and bladelike in posterior view; body of periotic swollen and smooth posteriorly.
Confused with: Physeteridae.
Typically found genera: None; most kogiid periotics found isolated have not been identified to the genus level.
Age: late Miocene to Pliocene (recent).
Distribution: Worldwide.
Established Localities: Yorktown Formation, Lee Creek Mine, North Carolina, USA; Bone Valley Formation, Florida.
Abundance: uncommon.
?Yorktown Formation, ?Pliocene, Lee Creek Mine, North Carolina, USA, CCNHM collections.
Ziphiidae
Size: Medium to Large (2.5-5+ cm)
Attributes: Short transversely inflated anterior process with blunt apex, separated from pars cochlearis by deep, dorsally facing anterior incisure; shallow to deep anterior bullar facet; large pars cochlearis and body together form proportionally enormous smoothly convex subspherical to ovoid shape; oval internal acoustic meatus with deeply recessed transverse crest; pars cochlearis markedly deeper than anterior process in medial view; small posterior process with equidimensional and smooth posterior bullar facet, typically curving or deflected ventrally.
Confused with: perhaps Physeteridae.
Typically found genera: Mesoplodon.
Age: middle Miocene to Pliocene (recent).
Distribution: Worldwide.
Established Localities: Yorktown Formation, Lee Creek Mine.
Abundance: Rare.
Unknown stratum, ?Miocene, Charleston lowcountry, South Carolina, USA, CCNHM collections.
Eoplatanistidae
Size: Small, 2-3 cm.
Attributes: Small overall size with proportionally large and hemispherical pars cochlearis, absurdly small anterior process, and ‘peaked’ body with acute angle formed between body and posterior process in medial view, ventrally deflected and proportionally small posterior bullar facet. Only a single genus is assigned to Eoplatanistidae, Eoplatanista, and its periotics are quite distinctive. Body lacks suprameatal fossa and superior ridge.
Confused with: Eurhinodelphinidae. Eurhinodelphinid periotics differ mostly by having a wider angle formed by the dorsal and posterior margins in medial view and by having a much larger and longer anterior process.
Typically found genera: Eoplatanista
Age: Early Miocene.
Distribution: Mediterranean, Western North Atlantic?
Established Localities: Belluno Sandstones of Italy.
Abundance: Locally uncommon in Charleston, South Carolina
(only).
Eurhinodelphinidae
Size: Small to medium (2.5-4 cm)
Attributes: Long, narrow, cylindrical anterior process (straight in ventral view) bearing distinctly concave, elongate and oval to rectangular anterior bullar facet, proportionally small and hemispherical pars cochlearis, and relatively small, short, leaf-shaped posterior bullar facet that is directed ventrally; body lacks suprameatal fossa and superior ridge. Hemispherical lateral tuberosity. A distinctive U or V-shaped sulcus (parabullary sulcus) is present on the ventrolateral surface of the anterior process.
Confused with: Eoplatanistidae.
Typically found genera: Eurhinodelphis, Schizodelphis, Xiphiacetus
Age: Early to middle Miocene, possibly late Oligocene.
Distribution: Worldwide.
Established Localities: Calvert and Choptank formations, Maryland and Virginia; Pungo River Limestone, North Carolina; early to middle Miocene strata of Belgium; Chilcatay Formation, Peru; Belluno Sandstone, Italy.
Abundance: Common on Atlantic coast; rare in North Pacific.
Squalodelphinidae
Size: Medium (3-4 cm)
Attributes: Long cylindrical and straight to medially bent anterior process, often with a medial tubercle, proportionally small and rectangular pars cochlearis with large and dorsomedially facing aperture for the cochlear aqueduct, small body with triangular gap between posterior process and lateral tuberosity, small square to trapezoidal and roughly equidimensional (short) posterior bullar facet.
Confused with: Pomatodelphine platanistoids.
Typically found genera: Notocetus, Phocageneus, Medocinia
Age: Early to middle Miocene, possibly late Oligocene.
Distribution: Worldwide.
Established Localities: Calvert and Choptank formations, Maryland and Virginia; Pungo River Limestone, North Carolina; Chilcatay Formation, Peru; Gaiman Formation, Argentina; Belluno Sandstone, Italy.
Abundance: Common to uncommon in North Atlantic; rare on
Pacific coast.
Allodelphinidae
Size: medium (3-4 cm)
Attributes: Large, inflated anterior process; large hemispherical pars cochlearis; small, tear-drop shaped internal acoustic meatus with raised rim; dorsal side of periotic with remnant suprameatal fossa developed as long sulcus; lateral surface of periotic transversely expanded (like Squalodontidae) at level of posterior pars cochlearis; highly reduced posterior process with posteroventrally facing, convex, smooth, and small posterior bullar facet.
Note: these features characterize Zarhinocetus, the only allodelphinid likely to be discovered by collectors. Ninjadelphis has a long posterior process, Allodelphis is similar to this, but these taxa are unlikely to be encountered as they are known by singleton specimens.
Confused with: Squalodelphinidae, Platanistidae
Typically found genera: Zarhinocetus
Age: early to late Miocene
Distribution: North Pacific
Established Localities: Sharktooth Hill Bonebed, California; Monterey Formation, California; Santa Margarita Sandstone, California.
Abundance: rare.
Pomatodelphinae (subfamily of Platanistidae)
Size: Medium to Large (3-5 cm)
Attributes: Long, highly inflated cylindrical and straight to medially bent anterior process, large and deep anterior bullar facet, hemispherical to rectangular pars cochlearis with endocranial opening of facial canal shifted lateral rather than anterior to vestibulocochlear opening (resulting in an internal acoustic meatus that has a nearly transverse rather than anteroposterior long axis), large articular rim, small, triangular to trapezoidal posterior bullar facet.
Confused with: Squalodelphinidae. Differs based on more grossly inflated anterior process and more acutely triangular gap between posterior process.
Typically found genera: Pomatodelphis, Zarhachis
Age: middle to late Miocene.
Distribution: North Atlantic.
Established Localities: Calvert Formation, Maryland and Virginia; Bone Valley Formation, Florida.
Abundance: Common.
Pontoporiidae
Size: Very Small (1.5-2 cm).
Attributes: Compact, small periotics with tiny anterior process and small, oval to square posterior bullar facet and proportionally enormous hemispherical pars cochlearis.
Confused with: Some Delphinidae, perhaps Phocoenidae.
Typically found genera: Pontoporia, Auroracetus
Age: Middle Miocene to Pliocene.
Distribution: North and South Atlantic.
Established Localities: Yorktown Formation, North Carolina; St. Marys Formation, Maryland/Virginia; Bone Valley Formation, Florida; Pliocene deposits, Belgium/Netherlands.
Abundance: Rare.
Lipotidae
Size: Medium (2.5-3.5 cm).
Attributes: Massive anterior process, triangular in ventral view, and bearing tubercle medially; proportionally large hemispherical pars cochlearis, small posteror process with tiny, deeply concave posterior bullar facet; body dorsoventrally deep, together with pars cochlearis forming trapezoidal shape; deep, large aperture for the vestibular aqueduct. Sword-like “styloid” process projecting from tip of anterior process (almost always broken in loose periotics). Ventral surface of anterior process deeply concave in lateral view; anterior bullar facet present.
Confused with: None, owing to location, but similar to some Kentriodontidae; differs from kentriodontids, and Delphinoidea, in possessing anterior bullar facet.
Typically found genera: Parapontoporia
Age: Late Miocene to Pliocene
Distribution: North Pacific
Established Localities: Purisima, San Diego, San Mateo, and Capistrano formations of California, and Almejas Formation of Baja California, Mexico.
Abundance: Common in California deposits. Most common odontocete
in Purisima Formation at Santa Cruz.
Kentriodontidae
Size: Small to large (1.5-5+ cm)
Attributes: Inflated anterior process typically with blunt apex and lacking anterior bullar facet; proportionally small and hemispherical pars cochlearis; lateral surface smooth and convex, lacking suprameatal fossa or groove; long posterior bullar facet concave, short to long. Generally differentiated from Delphinidae by longer anterior/posterior processes and proportionally smaller pars cochlearis; very difficult to differentiate from extinct genera Phocoenidae. Diverse family and diverse periotics, identifying to genus level frequently easier than to family, given that Kentriodontidae is probably paraphyletic or even polyphyletic.
Confused with: Delphinidae, Phocoenidae
Typically found genera: Delphinodon, Kentriodon, Liolithax, Hadrodelphis, Nannolithax; many additional named taxa
Age: late early Miocene to early late Miocene
Distribution: Worldwide
Established Localities: Calvert through St. Mary’s formations, Calvert Cliffs and beyond, Maryland/Virginia; Pungo River Limestone, Lee Creek Mine, North Carolina; Temblor Formation, Sharktooth Hill, California; Santa Margarita Sandstone, Santa Cruz, California; Astoria Formation, Oregon/Washington.
Abundance: Uncommon to common.
All from Yorktown Formation, Pliocene, Lee Creek Mine, North Carolina, USA, CCNHM collections.
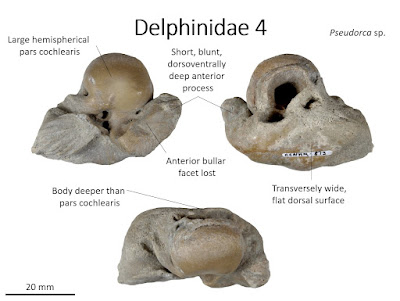
Delphinidae
Size: Small to very large (2-5+ cm)
Attributes: Proportionally small and blunt anterior process lacking anterior bullar facet; proportionally large to enormous circular (and frequently dorsoventrally shallow) pars cochlearis, sometimes with posteromedial bulge; smoothly convex and featureless dorsal surface of body lacking suprameatal fossa or groove, but occasionally possessing longitudinal ridge adjacent to dorsolaterally facing facet; internal acoustic meatus typically teardrop-shaped with anterolateral fissure for hiatus fallopii, and crista transversa deeply recessed into meatus; posterior process short with equidimensional, concave posterior bullar facets with deep (and lateral to posterolaterally directed) grooves/ridges for posterior process of bulla; posterior process with apex positioned laterally.
Confused with: Kentriodontidae, Monodontidae, Phocoenidae.
Typically found genera: Delphinus, Tursiops, Stenella, Globicephala, Pseudorca
Age: late Miocene through Pliocene (recent).
Distribution: Worldwide.
Established Localities: San Diego and San Mateo Formations, San Diego County, California; Yorktown Formation, Lee Creek Mine, North Carolina; Pliocene strata of Belgium & Netherlands; Plio-Pleistocene Red and Coralline Crag of UK; Pliocene of Australia/NZ.
Abundance: Rare to uncommon in North Pacific; common in
North Atlantic.
Monodontidae
Size: Medium to large (3-5 cm)
Attributes: Short, reduced, and blunt anterior process; proportionally enormous and anteriorly thrusted pars cochlearis; dorsoventrally thick body of periotic (elevated far dorsal to meatus) with transversely convex dorsolateral margin; in dorsal view, body of periotic widens posteriorly; large and transversely elongated internal acoustic meatus with high crista transversa; flat, ventrally facing small-medium sized leaf-shaped posterior bullar facet with anteroposteriorly (not posterolaterally) directed (and deep) ridges; entire periotic has triangular posterior margin as both the lateral and posterodorsal edges converge toward the posteriorly positioned apex of the posterior bullar facet.
Note: this is chiefly based on the beluga, Delphinapterus, and fossil monodontid periotics that seem similar to Delphinapterus; the narwhal, Monodon, possesses a much more delphinid-like periotic, and such examples are not yet known from the fossil record.
Confused with: Delphinidae, Albireonidae
Typically found genera: Delphinapterus, Bohaskaia, Denebola
Age: Late Miocene through Pliocene (recent)
Distribution: North Pacific and North Atlantic.
Established Localities: Almejas Formation, Baja California, Mexico; San Diego Formation, San Diego, California; Yorktown Formation, Lee Creek Mine, North Carolina.
Abundance: Rare in North Pacific; uncommon in North
Atlantic.
Albireonidae
Size: Medium (3-4 cm)
Attributes: Large, somewhat long and inflated/blunt anterior process, proportionally large, inflated, and hemispherical to subrectangular pars cochlearis (not anteriorly thrusted), large fenestra rotunda with a large nodule/expanse of bone posteromedial, often a posteromedial eminence on pars cochlearis; pars cochlearis (unlike Monodontidae) and body dorsoventrally deep (similar to Monodontidae); posterior process dorsoventrally quite deep (unlike Phocoenidae), deeper than Monodontidae; long, leaf-shaped posterior bullar facet.
Confused with: Phocoenidae, Monodontidae, Kentriodontidae
Typically found genera: Albireo
Age: late Miocene to Pliocene
Distribution: North Pacific
Established Localities: Almejas Formation, Baja California, Mexico.
Abundance: Very rare. Locally uncommon in Purisima Formation
at Santa Cruz, but unpublished.
Unknown stratum, Pliocene/Pleistocene?, Folly Beach, South Carolina, USA, CCNHM collections.
Purisima Formation, Pliocene, Santa Cruz, California, USA, UCMP collections.
Phocoenidae
Size: Small to medium (2-3 cm).
Attributes: Extant genera: Dorsoventrally narrow anterior process; low pars cochlearis; small, anteroposteriorly elongate posterior process that in medial view tapers posteriorly into a triangular point, similar to Monodontidae. Extinct forms approach the morphology of kentriodontids and delphinids and can be difficult to differentiate; tend to have proportionally large and anteriorly thrusted pars cochlearis, small posterior bullar facet. Identification to particular published genera is typically easier for extinct forms than identification to family. All phocoenids lack an anterior bullar facet, and all periotics smaller than Albireonidae. Tend to have longer anterior process and proportionally smaller pars cochlearis than Delphinidae.
Note: Phocoenids typically occur in strata that are younger entirely than kentriodontids, and tend to be rare where delphinids are common, such as the Atlantic coast Pliocene. Phocoenids are anomalously diverse in North Pacific and eastern South Pacific marine mammal assemblages.
Confused with: Albireonidae
Typically found genera: mostly unnamed, Piscolithax, ?Haborophocoena, ?Numataphocoena
Age: late Miocene to Pliocene
Distribution: North and South Pacific, North Atlantic (rare)
Established Localities: Numerous late Miocene and Pliocene localities in California (Purisima, Capistrano, San Diego, San Mateo formations), Almejas Formation of Baja California, Mexico; late Miocene-Pliocene localities in Japan; Pisco Formation of Peru
Abundance: Common in late Neogene Pacific localities; rare in Atlantic.
Others - Miscellaneous unusual periotics
I've added these mostly for folks to keep an eye out - these are unusual periotics from unusual dolphins that may or may not be found. Since they are unlikely to be found, I'll keep the commentary to a minimum.
Inticetus vertizi is a strange longirostrine "platanistoid" dolphin with archaeocete-like teeth from the late early Miocene Chilcatay Formation of Peru. Similar teeth in the tooth-taxon Phococetus are known from the late early Miocene of France as well as the Lee Creek Mine of North Carolina, and Phococetus is likely an inticetid. Though the teeth are extremely rare - four or five known altogether from the North Atlantic, including one in a private collection - periotics might be found. They roughly resemble squalodontid, waipatiid, and some aspects of eurhinodelphinid periotics. Image from Lambert et al. 2018.




























Wow! I have been searching for this type of descriptive information on whale and dolphin earbones for the last couple of years. This is extremely helpful and much appreciated.
ReplyDeleteThese posts are amazing. Over the years I've found several fossils I could recognize as periotics and tympanic bulla from sites along the Calvert Cliffs, but their functions for cetacean hearing were never very clear to me, now they are. Further, I just acquired an old collection of fossils collected at Plum Point, MD, that includes many dolphin earbones. So your two posts are a godsend. I may even manage an ID or two. Thank you.
ReplyDelete